Localized properties#
ESP charges#
Since there is no unique definition for partial charges and no corresponding physical observable, they can be assigned in several ways, such as being derived from the quantum mechanical electrostatic potential
that can be replaced with a potential caused by the partial charges:
The Merz–Kollman scheme minimizes the squared norm difference between these two quantities evaluated on a set of grid points in the solvent-accessible region of the molecule with respect to variations in the partial charges and a constraint of a conservation of the total molecular charge – the grid points are distributed on successive layers of scaled van der Waals surfaces. This measure is referred to as the figure-of-merit
The resulting electrostatic potential (ESP) charges are obtained by solving the equation
where
and
Python script
import veloxchem as vlx
xyz_str = """6
Methanol
H 1.2001 0.0363 0.8431
C 0.7031 0.0083 -0.1305
H 0.9877 0.8943 -0.7114
H 1.0155 -0.8918 -0.6742
O -0.6582 -0.0067 0.1730
H -1.1326 -0.0311 -0.6482
"""
molecule = vlx.Molecule.read_xyz_string(xyz_str)
basis = vlx.MolecularBasis.read(molecule, "6-31G*")
esp_drv = vlx.EspChargesDriver()
esp_drv.equal_charges = "1=3, 1=4"
esp_charges = esp_drv.compute(molecule, basis)
Download a Python script type of input file to calculate the ESP charges for the water molecule at the HF/6-31G level of theory.
Text file
@jobs
task: esp charges
@end
@method settings
basis: 6-31G*
@end
@molecule
charge: 0
multiplicity: 1
xyz:
...
@end
Download a text file type of input file to calculate the ESP charges for the water molecule at the HF/6-31G level of theory.
In both cases, the user can control the number of layers of the molecular surface as well as the surface grid point density in these layers (in units of Å\(^{-2}\)). In the above examples, the recommended default values are employed.
RESP charges#
The restrained electrostatic potential (RESP) charge model is an improvement to the Merz–Kollman scheme as the figure-of-merit \(\chi^2_\mathrm{esp}\), is rather insensitive to variations in charges of atoms buried inside the molecule, as illustrated below for methanol and its buried carbon atom in red.
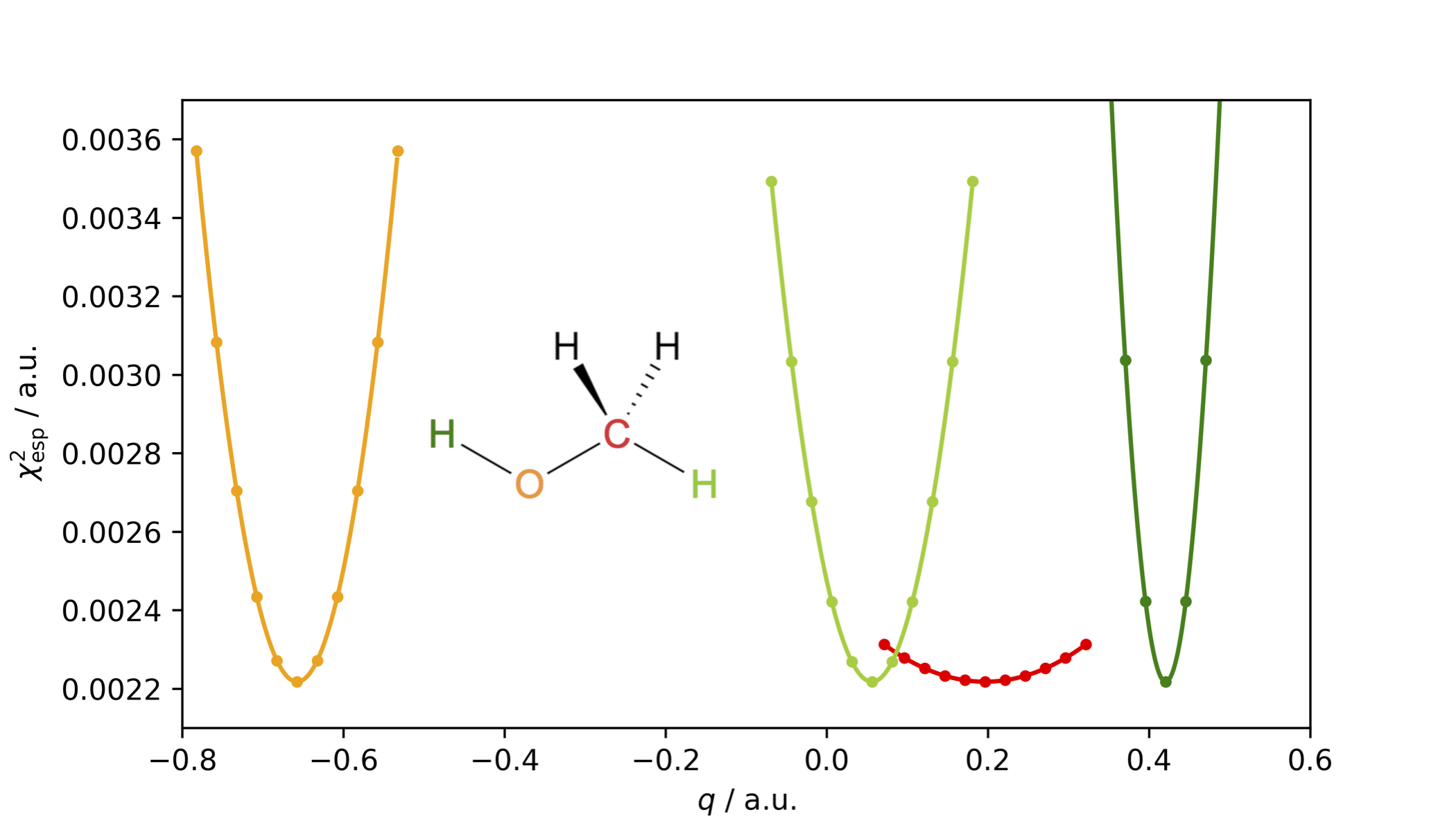
To avoid unphysically large charges of interior atoms, a hyperbolic penalty function is added
so that the diagonal matrix elements become equal to
with a dependency on the partial charge. Consequently, RESP charges are obtained by solving the matrix equation iteratively until the charges and Lagrange multipliers become self-consistent. In addition to that, the RESP charge model allows for the introduction of constraints on charges of equivalent atoms due to symmetry operations or bond rotations.
Python script
import veloxchem as vlx
xyz_str = """6
Methanol
H 1.2001 0.0363 0.8431
C 0.7031 0.0083 -0.1305
H 0.9877 0.8943 -0.7114
H 1.0155 -0.8918 -0.6742
O -0.6582 -0.0067 0.1730
H -1.1326 -0.0311 -0.6482
"""
molecule = vlx.Molecule.read_xyz_string(xyz_str)
basis = vlx.MolecularBasis.read(molecule, "6-31G*")
resp_drv = vlx.RespChargesDriver()
resp_drv.equal_charges = "1=3, 1=4"
resp_charges = resp_drv.compute(molecule, basis)
Download a Python script type of input file to calculate the RESP charges for the water molecule at the HF/6-31G* level of theory.
Text file
@jobs
task: resp charges
@end
@method settings
basis: 6-31g*
@end
@resp charges
equal charges: 2 = 3 ! with reference to the atom ordering below
@end
@molecule
charge: 0
multiplicity: 1
xyz:
...
@end
Download a text file type of input file to calculate the RESP charges for the water molecule at the HF/6-31G* level of theory.
Boltzmann-weighted RESP charges#
It is also possible to calculate the Boltzmann-weighted RESP charges for a set of conformers.
Python script
Below, the argument conformers is a list of molecule objects for which the averaging is performed. By default, the calculation is performed at the Hartree–Fock level using the 6-31G* basis set.
resp_drv = vlx.RespChargesDriver()
resp_charges = resp_drv.compute(conformers)
Download a Python script type of input file to calculate the Boltzmann-weighted RESP charges for the three conformers of propanol at the HF/6-31G* level of theory.
Text file
@jobs
task: resp charges
@end
@method settings
basis: 6-31g*
@end
@resp charges
xyz_file: all_conformers.xyz
@end
@molecule
charge: 0
multiplicity: 1
@end
Download a text file type of input file to calculate the Boltzmann-weighted RESP charges for the three conformers of propanol at the HF/6-31G* level of theory, and use the all_conformers.xyz file.
CHELPG charges#
Different choices of grid points in the Merz–Kollman (MK) scheme can be made. CHELPG charges are obtained with grid points chosen on a dense cubic grid with exclusion made of grid points inside the van der Waals molecular volume.
In contrast to the original MK scheme, the calculation of CHELPG charges involve grid points directly outside the van der Waals molecular volume, and since the electrostatic potential is here large, these points will be important for the minimization of the Lagrangian. We note that there is no universal grid-point choice that can be considered best for all situations.
Python script
import veloxchem as vlx
xyz_str = """6
Methanol
H 1.2001 0.0363 0.8431
C 0.7031 0.0083 -0.1305
H 0.9877 0.8943 -0.7114
H 1.0155 -0.8918 -0.6742
O -0.6582 -0.0067 0.1730
H -1.1326 -0.0311 -0.6482
"""
molecule = vlx.Molecule.read_xyz_string(xyz_str)
basis = vlx.MolecularBasis.read(molecule, "6-31G*")
esp_drv = vlx.EspChargesDriver()
esp_drv.grid_type = "chelpg"
esp_drv.equal_charges = "1=3, 1=4"
chelpg_charges = esp_drv.compute(molecule, basis)
Charge comparison#
The localized charges for methanol in the examples above become:
Atom ESP charge RESP charge CHELPG charge
--------------------------------------------------------
H 0.023220 0.033747 0.003200
C 0.148458 0.118610 0.225480
H 0.023220 0.033747 0.003200
H 0.023220 0.033747 0.003200
O -0.594785 -0.639004 -0.611345
H 0.376669 0.419154 0.376265
--------------------------------------------------------
Total: 0.000000 0.000000 -0.000000
LoProp charges and polarizabilities#
The LoProp approach [GLKarlstrom04] is implemented for the determination of localized (atomic) charges and polarizabilities that enter into polarizable embedding calculations of optical spectra.
Python script
import veloxchem as vlx
molecule = vlx.Molecule.read_molecule_string(
"""
O 0.0000000 0.0000000 -0.1653507
H 0.7493682 0.0000000 0.4424329
H -0.7493682 0.0000000 0.4424329
"""
)
basis = vlx.MolecularBasis.read(molecule, "ANO-S-VDZP")
scf_drv = vlx.ScfRestrictedDriver()
scf_results = scf_drv.compute(molecule, basis)
loprop_drv = vlx.PEForceFieldGenerator()
loprop_results = loprop_drv.compute(molecule, basis, scf_results)
This calculation gives the following results.
LoProp charges (a.u.):
O: -0.6777
H: 0.3388
H: 0.3388
LoProp polarizabilities (a.u.):
xx yy zz
O: 3.88 2.91 3.69
H: 1.84 1.21 1.57
H: 1.84 1.21 1.57
Download a Python script type of input file to calculate the LOPROP charges and atomic polarizabilities for the water molecule at the B3LYP/ANO-S-VDPZ level of theory.
Text file
@jobs
task: loprop
@end
@method settings
xcfun: b3lyp
basis: ANO-S-VDZP ! An ANO type of basis set should be used
@end
@molecule
charge: 0
multiplicity: 1
xyz:
...
@end
Download a text file the input file to calculate the LoProp charges and atomic polarizabilities for the water molecule at the B3LYP/ANO-S-VDPZ level of theory.